Understanding Penile Lymphedema: An In-Depth Analysis

Intro
Penile lymphedema represents a topic often overlooked in medical discussions. Its prevalence is not well-documented, leading to a lack of awareness regarding its implications. This condition manifests as localized swelling in the penile area, resulting from impaired lymphatic drainage. Understanding the underlying mechanisms, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for both medical professionals and patients.
This article aims to provide an extensive overview, addressing the anatomy of the lymphatic system, the various causes leading to penile lymphedema, potential complications, and the different treatment options available. The exploration extends to associated comorbidities, diagnostic methods, and future research directions, ensuring a rounded comprehension of this delicate issue.
Key Concepts
Definition of Primary Terms
Penile lymphedema is characterized by an abnormal accumulation of lymphatic fluid in penile tissues. The lymphatic system plays a pivotal role in maintaining fluid balance and immune function. When this system is compromised, it can lead to conditions like lymphedema. Understanding these terms lays the foundation for recognizing the severity and implications of penile lymphedema.
Related Concepts and Theories
Different theories explain the etiology of lymphedema. Primary lymphedema arises from congenital malformations, while secondary lymphedema results from external factors such as surgery, trauma, or infection. The link between penile lymphedema and conditions like obesity and diabetes is also notable, as these factors can exacerbate fluid buildup. Recognizing these interrelated concepts is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Etiology and Mechanism
The causes of penile lymphedema can vary significantly. Common etiological factors include infection, malignancy, and trauma. In addition, surgical procedures, particularly those affecting the lymphatic system, can lead to disruptions that provoke the development of lymphedema.
An understanding of the lymphatic anatomy is crucial to visualize how these factors contribute to the condition. The lymphatic vessels in the genital area drain lymph from surrounding tissues. Any obstruction in this flow can result in swelling.
Complications and Consequences
The complications associated with penile lymphedema are significant. Patients may experience discomfort, pain, and psychological distress. The swollen region is also more susceptible to infections and skin conditions, which can further complicate treatment strategies. Moreover, the implications on sexual health and overall quality of life should not be underestimated.
Management Strategies
Effective management begins with diagnosing the underlying cause. Treatment options vary based on severity and etiology. Non-surgical approaches include compression therapy, exercises, and lifestyle modifications such as weight management. Surgical options might be necessary in severe cases where conservative measures fail.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosis can be a multifaceted approach that often involves imaging studies and clinical evaluations. These may include lymphoscintigraphy, ultrasound, or MRI, which help to visualize lymphatic flow and identify abnormalities.
Future Directions
Gaps Identified in Current Research
Despite its clinical significance, there are notable gaps in the research on penile lymphedema. Most studies focus on lymphedema in other parts of the body, leaving a knowledge gap specific to the penile region. More targeted research could elucidate the best management practices and quality of life issues for affected individuals.
Suggestions for Further Studies
Future studies should aim to collect data on prevalence and long-term outcomes of patients with penile lymphedema. Additionally, examining the psychological impact and exploring innovative management techniques could enrich the current body of knowledge.
Understanding penile lymphedema can improve patient outcomes and enhance the quality of care provided.
By engaging in a thorough exploration of this condition, we can strive not only to advance clinical practices but also to shed light on a critical aspect of men's health that has been largely ignored.
Prelude to Penile Lymphedema
Penile lymphedema often remains a topic of limited discussion in medical literature despite its significance. The increasing prevalence of conditions that can lead to lymphatic dysfunction, along with the impacts on quality of life, calls for greater awareness and understanding. This introduction aims to set the stage for a comprehensive examination of penile lymphedema.
The implications of penile lymphedema stretch beyond the physical manifestations to affect psychological well-being and interpersonal relationships. Recognizing and contextualizing this condition within a broader medical framework is vital for healthcare providers. As the lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance and immunity, understanding its dysfunction is particularly important when discussing the development of penile lymphedema.
This section will delve into the specific characteristics of penile lymphedema and highlight its relevance in both medical practice and personal health management. Additionally, it will underscore the need for empathetic care of patients experiencing this condition, therefore contributing to a well-rounded understanding of its complexities.
Defining Penile Lymphedema
Penile lymphedema refers to the buildup of lymphatic fluid in the penile region, leading to localized swelling. This condition arises when normal lymphatic drainage is disrupted. Several factors can cause this disruption, which include trauma, surgical interventions, infections, or congenital abnormalities. The manifestation of penile lymphedema can vary from mild swelling to more significant enlargement, which may impact both physical comfort and psychological well-being.
The symptoms of penile lymphedema can lead to complications. These complications can include a higher risk of infection, changes in urination, and discomfort during sexual activities.
The Importance of Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system serves multiple critical functions in the body. It is responsible for maintaining fluid balance, filtering out pathogens, and transporting waste products. The system comprises lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph fluid. When this intricate network faces impairment, the consequences are multifaceted.
In regard to penile lymphedema, a dysfunctional lymphatic system results in lymph accumulation. This accumulation can manifest in different ways, from swelling to skin changes. Understanding the significance of this system enables one to appreciate the underlying causes and implications of penile lymphedema. Moreover, it emphasizes the necessity of appropriate diagnostic and treatment approaches in managing the condition effectively.
Anatomy of the Penile Region
Understanding the anatomy of the penile region is crucial in addressing penile lymphedema. The anatomy directly affects the lymphatic drainage, vascular supply, and innervation, all of which have significant implications for both diagnosis and management of this condition. A clear grasp of these anatomical structures ensures accurate assessments, aids in effective treatment strategies, and enhances communication among medical professionals.
Lymphatic Drainage Pathways
The lymphatic system is a vital component of fluid balance in the body. In the penile region, lymphatic drainage primarily occurs through a network of lymphatic vessels. These vessels play a key role in transporting lymph, which contains excess fluid, proteins, and waste products away from tissues.

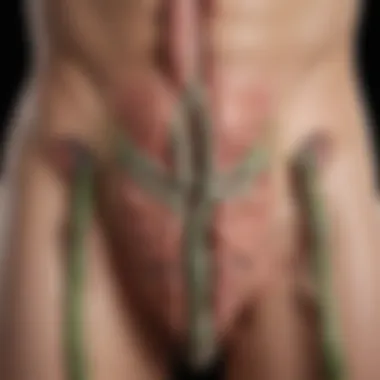
The primary nodes involved in penile lymphatic drainage include inguinal lymph nodes and pelvic lymph nodes. The lymphatic vessels originate from the glans and the shaft and eventually drain into these nodes, which can become significant in understanding the potential complications of penile lymphedema.
The lymphatic pathways can become disrupted due to various factors, such as trauma or surgical procedures. Impairment in these pathways can lead to an accumulation of lymphatic fluid, resulting in swelling. Therefore, recognizing this anatomical detail is essential in both the diagnosis and subsequent management of lymphedema.
Vascular Supply and Innervation
The vascular supply of the penis is chiefly provided by the internal pudendal artery, a branch of the internal iliac artery. This arterial supply is essential not only for normal function but also for the maintenance of tissue health. Any disruption in this blood supply can have repercussions on the lymphatic system as well. Additionally, the veins, which include the dorsal vein and deep dorsal veins, work in tandem with the arteries to ensure proper drainage of blood and lymphatic fluid.
Nerve supply is primarily derived from the sacral plexus and the pudendal nerve. This innervation plays a role in both sensory perception and autonomic control of the penile tissues. Impacts on this nerve supply can lead to various issues, including erectile dysfunction, exacerbating the psychosocial effects of penile lymphedema.
Overall, comprehending the vascular and innervation aspects of the penile region underscores the interconnectedness of these systems. Anomalies or damage to these anatomical structures necessitate a more sophisticated approach in managing penile lymphedema effectively.
Etiology of Penile Lymphedema
Understanding the etiology of penile lymphedema is essential for identifying its causes, which can aid in effective management and treatment. The causes of this condition can be classified as congenital or acquired, each contributing to how the lymphatic system functions within the penile region. Recognizing these factors can lead to earlier detection, better treatment outcomes, and enhanced patient education.
Congenital Factors
Congenital factors may play a fundamental role in the development of penile lymphedema. These factors are present at birth and can be attributed to genetic conditions that affect lymphatic development. Common congenital conditions include lymphatic dysplasia or syndromes that impair normal lymphatic function. In such cases, lymphatic vessels are either absent or not properly formed, leading to inadequate drainage of lymph fluid.
Some specific congenital conditions include:
- Milroy's Disease: A disorder characterized by hereditary lymphedema due to mutations affecting the lymphatic system.
- Turner Syndrome: A genetic condition in females involving the absence of one X chromosome, often featuring lymphedema due to lymphatic abnormalities.
These congenital issues emphasize the necessity for tailored screening in at-risk populations, promoting early intervention strategies to manage the lymphatic health of patients.
Acquired Causes
Acquired causes of penile lymphedema are often more prevalent and can arise from various environmental, medical, or surgical interventions. Addressing these factors is critical, as they are often modifiable. Some of the common acquired causes include:
- Infections: Conditions such as filariasis can severely affect lymphatic function.
- Trauma or Surgery: Surgical procedures, particularly those involving pelvic surgery or cancer treatment, can damage lymphatic channels, leading to lymphedema.
- Cancer: Tumors in the pelvic region might press on or invade lymphatic vessels, obstructing normal drainage.
- Obesity: Excessive body weight increases pressure on lymphatic vessels, impairing drainage.
Identifying the specific acquired cause can significantly impact treatment protocols. For instance, if surgery is the underlying issue, a multidisciplinary approach to patient care may be necessary to address both the surgical site and any resultant lymphatic complications.
"Understanding the causes of penile lymphedema is vital in guiding therapeutic decisions and potentially improving the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition."
In summary, both congenital and acquired factors play pivotal roles in the etiology of penile lymphedema. Recognizing these factors can help inform clinical practice and support improved management strategies for patients suffering from this condition.
Clinical Presentation
The clinical presentation of penile lymphedema serves as a critical component in understanding this medical condition. Recognizing the symptoms and the ways in which penile lymphedema manifests can significantly aid healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing this ailment effectively. This section delves into the essential aspects of clinical presentation, including symptoms and how to differentiate penile lymphedema from other similar conditions. Understanding these elements not only enhances clinical diagnosis but also helps in educating patients about what they should watch for and when to seek medical attention.
Symptoms of Penile Lymphedema
Penile lymphedema is commonly marked by a range of symptoms that primarily revolve around swelling in the penile region. The once normal appearance of the area may change due to several factors. Commonly reported symptoms include:
- Localized Swelling: This is the hallmark of penile lymphedema. The swelling may vary in severity and can present as a soft or firm enlargement that may expand over time.
- Discomfort or Pain: Affected individuals might experience discomfort or pain, particularly during activities such as urination or sexual intercourse. The sensations can range from mild to acute, depending on the severity of the condition.
- Skin Changes: The skin over the swollen area might undergo alterations. This may include thickening, discoloration, or the development of lesions.
- Reduced Mobility: In severe cases, the swelling can restrict the range of motion, making normal movement difficult.
- Increased Infections: There is a higher risk of opportunistic infections due to compromised tissue integrity. Patients may deal with recurrent infections that can complicate the condition.
A timely assessment of these symptoms is paramount. Early diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment options and help mitigate potential complications associated with the condition.
Differentiating from Other Conditions
Distinguishing penile lymphedema from other similar conditions is essential for effective management and treatment. There are various conditions that may present symptoms resembling penile lymphedema, including:
- Hydrocele: This condition involves fluid buildup around the testicles and can cause similar swelling. A hydrocele typically presents with a different consistency and location of swelling compared to lymphedema.
- Varicocele: This condition arises when veins within the scrotum become enlarged. It may lead to discomfort and swelling but is different in its vascular origin.
- Infections: Conditions such as balanitis or cellulitis can cause localized swelling and pain. Recognizing accompanying symptoms such as fever can assist in diagnosis.
- Neoplasms: Tumors, whether benign or malignant, can also present with swelling in the area. Imaging studies may be necessary to differentiate neoplastic growths from lymphedema.
A thorough clinical evaluation often involves a comprehensive history and physical examination, supported by imaging studies where necessary, to confirm the diagnosis. Understanding these differentiating factors empowers healthcare professionals to develop appropriate treatment strategies for those affected.
Diagnosis of Penile Lymphedema
The diagnosis of penile lymphedema is a crucial step in managing this condition effectively. It requires a thorough understanding of both clinical symptoms and diagnostic methodologies available. Accurate diagnosis allows health professionals to develop a tailored treatment plan, minimizing complications and optimizing patient outcomes. Because penile lymphedema can mimic other conditions, distinguishing it through careful evaluation is essential. Failure to diagnose correctly could lead to inappropriate treatments, exacerbating the symptoms or causing further issues.
Clinical Evaluation Techniques
Clinical evaluation plays a pivotal role in diagnosing penile lymphedema. Physicians conduct a comprehensive patient history to gather relevant information about symptoms, onset, and duration. Documenting any previous conditions affecting the lymphatic system or vascular integrity is vital.
Physical examination follows, where the clinician assesses the penis and surrounding tissues. Key indicators include:
- Swelling: An observable increase in size or volume of the penile region.
- Texture Changes: The skin may show thickening or induration due to fluid accumulation.
- Pain or Discomfort: Sensations reported by the patient during examination can indicate lymphedema.
Additional tests, like the assessment of lymphatic function and swelling patterns, may help clarify the diagnosis. In some cases, healthcare providers may suggest a referral to a specialist in lymphatic disorders for further evaluation.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are valuable tools in confirming the diagnosis of penile lymphedema. They provide insights that physical examination alone may not reveal. Commonly utilized imaging techniques include:
- Ultrasound: This modality helps visualize lymphatic pathways and any underlying structures that might contribute to lymphedema. It can show fluid accumulation or obstructions.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI gives a detailed view of soft tissues, which aids in identifying any complications or concomitant conditions.
- Lymphoscintigraphy: This specialized imaging involves injecting a radioactive tracer to visualize lymphatic flow. It is particularly effective in determining if lymphatic channels are blocked.


Incorporating these advanced imaging techniques ensures a comprehensive assessment of the penile region, supporting a definitive diagnosis. Accurate imaging facilitates informed clinical decisions, ultimately guiding effective management of penile lymphedema.
Accurate diagnosis is critical for treatment efficacy in penile lymphedema.
Complications of Penile Lymphedema
Complications arising from penile lymphedema can be significant, impacting not just physical health but also psychological well-being and social interactions. Understanding these complications is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike. This section will explore two main complications: infection risks and impacts on sexual function. Recognizing these issues helps in creating comprehensive management strategies that can enhance patient quality of life.
Infection Risks
One of the primary complications of penile lymphedema is the heightened risk of infections. When lymphatic drainage is compromised, fluids may accumulate in the tissues. This can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth, especially if the skin integrity is compromised.
Infections associated with penile lymphedema can manifest as:
- Balanitis: Inflammation of the glans which may lead to discomfort and increase the risk of further complications.
- Cellulitis: A serious bacterial skin infection that can cause swelling, redness, and pain in the affected area.
- Lymphedema-associated dermatitis: Skin changes that arise due to prolonged swelling, increasing susceptibility to infections.
Patients must be vigilant for signs of infection, including increased redness, warmth, tenderness, or discharge. Prompt medical treatment is essential as untreated infections can lead to severe complications. Regular monitoring and maintaining proper hygiene play key roles in prevention.
Impact on Sexual Function
Penile lymphedema can also significantly affect sexual function. The physical changes and discomfort associated with lymphedema may result in psychological stress, which in turn can impact intimate relationships and sexual performance.
Consequences related to sexual function can include:
- Erectile dysfunction: Physical discomfort and psychological factors from lymphedema can contribute to difficulties in achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Painful intercourse (dyspareunia): The swelling can lead to painful sensations during sexual activity, which may deter sexual engagement.
- Psychological effects: Feelings of self-consciousness or anxiety can stem from visible changes or discomfort, further complicating intimate relationships.
These complications underline the importance of addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of penile lymphedema. Open communication with healthcare providers can aid in finding appropriate management strategies. Effective treatment can mitigate these risks and help maintain a healthy sexual life.
The interplay between physical health and emotional well-being in patients with penile lymphedema cannot be overstated. Adequate management strategies address the complexities involved, ultimately enhancing overall quality of life.
Management Strategies for Penile Lymphedema
Effective management strategies for penile lymphedema are crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected by this condition. Addressing this issue requires a nuanced understanding of the available options, which can range from conservative measures to more invasive surgical interventions. Each strategy presents its own set of benefits and considerations that need careful evaluation. A comprehensive approach can help mitigate symptoms, reduce complications, and enhance overall wellbeing.
Conservative Management Approaches
Conservative management involves non-surgical techniques aimed at alleviating symptoms and promoting lymphatic function. These approaches can be particularly beneficial in mild to moderate cases. Some of the key elements include:
- Compression Therapy: Use of compression garments can help reduce swelling by promoting fluid movement out of the affected area. These garments must be worn as directed for maximum effectiveness.
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD): This is a specialized form of massage that encourages lymph fluid to flow more freely. Trained therapists typically perform MLD, resulting in potential swelling reduction.
- Exercise Regimens: Engaging in regular, moderate exercises like walking or swimming can facilitate lymphatic drainage. Exercise should always be tailored to individual capabilities to avoid injury.
- Skin Care: Maintaining good skin hygiene and applying moisturizers can reduce the risk of infections, which is essential as lymphedema can impair skin integrity.
- Dietary Adjustments: Following a low-sodium diet can help manage fluid retention. Increased hydration and a diet rich in antioxidants may also be beneficial.
Incorporating these methods into daily routines can lead to significant improvements in symptoms. Patients must work closely with their healthcare providers to develop personalized management plans that consider individual needs and preferences.
Surgical Interventions
When conservative approaches do not yield satisfactory results, surgical options may be considered. Surgical interventions are typically reserved for more severe cases, and they can offer rapid relief from symptoms. Surgical strategies often include:
- Lymphatic Bypass Surgery: This procedure creates a pathway for lymph fluid to circumvent blocked areas, promoting better drainage and reducing swelling.
- Liposuction: In cases of significant lymphedema, liposuction can be performed to remove excess tissue that has accumulated as a result of chronic swelling.
- Debulking Surgery: This aims to remove enlarged tissue in the penile region to improve functionality and aesthetics, although it may not always restore full lymphatic drainage.
- Flap Surgery: This may involve transferring tissue from other parts of the body to reconstruct the affected area and improve drainage.
Each surgical intervention carries risks and benefits that need thorough discussion with a medical professional. The decision to undergo surgery should be made after evaluating the severity of the condition and the expected outcomes.
Patients should be aware that while surgical options can provide relief, they often require physical rehabilitation and long-term follow-up to optimize results.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle modifications play an integral role in managing penile lymphedema. This condition often manifests through swelling, discomfort, and even complications that may hinder daily activities and affect overall well-being. By adopting specific lifestyle changes, individuals can effectively reduce symptoms and potentially mitigate the complications associated with lymphedema.
These modifications encompass various aspects of daily life, primarily focusing on dietary considerations and physical activity guidelines. Both of these elements significantly influence the management of lymphedema. Here, we will explore them in detail, emphasizing their importance and advantages.
Dietary Considerations
Diet plays a crucial role in managing penile lymphedema. A balanced diet can help reduce inflammation and improve lymphatic function. Key considerations include:
- Hydration: It is vital to maintain adequate fluid intake. Proper hydration can facilitate lymphatic drainage and prevent excessive swelling.
- Low-sodium Diet: Reducing sodium intake helps minimize fluid retention, which can exacerbate lymphedema symptoms. Individuals should be cautious of processed foods that often contain high levels of sodium.
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Consuming foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, may help control inflammation. Foods like berries, spinach, and nuts provide beneficial nutrients that support lymphatic health.
- Balanced Macronutrients: Adequate protein intake is important for tissue repair and regeneration. Similarly, healthy fats, like those from avocados and olive oil, can contribute positively to overall health.
"Dietary changes are not just about restriction. They play a pivotal role in restoring balance within the body and supporting overall health, especially in lymphedema management."
Making these dietary adjustments is fundamental as they set the stage for improved lymphatic function and can significantly mitigate the severity of symptoms associated with penile lymphedema.
Physical Activity Guidelines
Engaging in physical activity is another crucial aspect of lifestyle modifications for individuals with penile lymphedema. Exercise promotes lymphatic flow, reduces swelling, and enhances emotional well-being. Here are some essential guidelines:
- Regular Exercise: Participating in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly can be beneficial. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are generally well-tolerated activities that encourage circulation.
- Strength Training: Incorporating strength training exercises two days a week helps build muscle, which in turn assists lymphatic drainage. It is important to start with light weights and gradually increase resistance while monitoring for any adverse effects.
- Lymphatic Drainage Exercises: Specific exercises designed to stimulate lymphatic function can be introduced. These include gentle stretching and movements that focus on the lower body, as the lymphatic system relies heavily on muscle contractions to function effectively.
- Listen to Your Body: Individuals must remain aware of their body's limits. If swelling increases after certain activities, adjustments should be made to avoid exacerbation of symptoms.
Psychosocial Impacts


The psychosocial aspects of penile lymphedema are crucial to overall patient outcomes. This condition not only affects physical well-being but also has significant implications for mental health and social interactions. Understanding these impacts is essential for a holistic approach to treatment and care.
Mental Health Considerations
Penile lymphedema can lead to feelings of anxiety and depression. Patients often grapple with the physical changes and discomfort that come with the condition, which can create an internal struggle. Studies show that men with visible genital conditions may experience lower self-esteem and body image issues.
Accessing mental health support can be a vital step for patients. Therapy may help them process their feelings and develop coping strategies. Support groups can also provide an understanding environment where men can share experiences. It's critical for healthcare providers to screen for mental health issues in patients with penile lymphedema to ensure comprehensive care.
Social Stigmas and Support Systems
Social stigma surrounding genital conditions can exacerbate feelings of isolation. Men suffering from penile lymphedema may avoid social gatherings or intimate relationships. The fear of judgment or misunderstanding can hinder their willingness to discuss the condition openly.
Having a strong support system is vital. This can include friends, family, or even online communities. Such networks offer emotional support and practical advice, ensuring that patients do not face their challenges alone. Encouraging open dialogue about penile health can help mitigate stigma, fostering a more accepting atmosphere.
"The societal silence around male genital conditions only perpetuates the stigma, making it essential to advocate for awareness and support."
In summary, addressing the psychosocial impacts of penile lymphedema is as important as the clinical treatment itself. Active support and awareness can lead to improved quality of life for affected individuals.
Current Research and Advances
Research into penile lymphedema is gaining more attention, emphasizing its relevance in medical literature. Recent studies have shed light on the physiological mechanisms behind lymphatic drainage and how these can be disrupted in this specific context. Understanding these nuances helps in developing targeted treatment protocols. As lymphedema can result from various factors, each case may present unique challenges.
The integration of recent findings into clinical practice could potentially improve patient outcomes significantly. Thus, ongoing research is essential, not only for enhancing our knowledge but also for shaping effective management strategies.
Innovative Treatment Options
Innovative treatments are emerging in the field of penile lymphedema. These range from minimally invasive procedures to advanced therapies aimed at restoring lymphatic function. One significant option is lymphatic microsurgery, which has shown promising results in certain cases. Techniques such as lymphovenous anastomosis allow for bypassing damaged lymphatic vessels, thereby restoring fluid balance effectively.
In addition to surgical interventions, new pharmacological therapies are under investigation. Research is exploring the efficacy of medications that enhance lymphatic drainage or reduce swelling. For example, certain diuretics can help manage fluid retention, but their long-term effects specifically on penile lymphedema are yet to be fully understood.
Furthermore, the utilization of compression therapy is being refined. Recent studies suggest that personalized compression garments may provide better outcomes compared to generic options. This tailored approach can enhance patient comfort and compliance.
Recent advancements in physiotherapy techniques also show potential. Manual lymphatic drainage therapy is being adapted to suit the needs of patients with penile lymphedema, presenting a non-invasive option to alleviate symptoms and improve lymphatic circulation.
Future Research Directions
Looking ahead, the direction of future research into penile lymphedema is crucial. There is a clear need for larger clinical trials to substantiate the efficacy of existing treatments and explore new ones. Research should focus on identifying genetic and environmental risk factors that may predispose individuals to this condition. A deeper understanding could lead to earlier interventions and more effective preventative strategies.
Moreover, studying the psychosocial impacts of penile lymphedema remains a vital area of exploration. The emotional and psychological burdens faced by patients are profound, affecting their quality of life. Further research is needed to develop holistic approaches that integrate mental health support alongside physical treatment.
Technological advancements offer opportunity as well. Utilizing imaging techniques could allow for better diagnostics, helping to differentiate between penile lymphedema and other conditions. This precision in diagnosis can enhance treatment plans and patient outcomes.
Research collaborations across disciplines, including urology, lymphology, and psychology, are essential to approach penile lymphedema comprehensively. Interdisciplinary teams can better address the multifaceted nature of this condition, offering patients a more integrated care pathway.
Discussion
The topic of discussion holds significant relevance in understanding penile lymphedema. It is an avenue for professionals and students alike to exchange insights, challenge prevailing paradigms, and potentially innovate approaches to diagnosis and management. This section aims to synthesize expert opinions and integrate empirical research into clinical practice, forming a bridge between theory and application. By doing so, we explore the multifaceted dimensions of penile lymphedema, emphasizing how comprehensive discourse can enhance patient care and the understanding of this often overlooked condition.
Expert Opinions and Perspectives
Clinical experts contribute invaluable insights that shed light on various aspects of penile lymphedema. Their observations often illuminate the gaps in existing literature and clinical practices. Many professionals assert that more awareness is needed to address misconceptions regarding the condition.
The significance of proper diagnosis is a prominent point in expert discussions. Misdiagnosis can lead to inadequate treatment plans, which, in turn, aggravate patients’ suffering. Experts advocate for a more rigorous approach in training healthcare providers, ensuring they recognize symptoms and understand the underlying mechanisms of lymphatic dysfunction.
Additionally, interdisciplinary collaboration is frequently mentioned. Engaging urologists, lymphologists, and physical therapists can lead to a well-rounded understanding of the condition and its management. This collaborative approach helps in formulating a multi-faceted treatment strategy, incorporating both physiological and psychosocial considerations.
Integration of Research and Practice
The integration of research findings into clinical practice is critical for advancing the understanding of penile lymphedema. Ongoing studies focus on various aspects such as genetic predispositions, potential biomarkers, and novel therapeutic interventions. Keeping abreast of the latest research can significantly improve outcome measures for patients.
Clinical practitioners are encouraged to incorporate evidence-based protocols in their routine practice. This involves
- Utilizing updated diagnostic criteria: Ensuring the most current research is reflected in clinical guidelines for diagnosis and management.
- Applying novel treatments: Research has begun to explore advanced therapies, such as enzymatic decongestion and lymphatic drainage massage, indicating potential benefits.
- Monitoring long-term outcomes: Collecting data on patient progress can help refine approaches and establish best practices.
By fostering a dialogue between researchers and clinicians, the field can evolve more rapidly. This synergy ultimately enhances patient outcomes, reduces complications, and improves the overall quality of care in managing penile lymphedema. Recent works highlighted in journals, like the Journal of Urology, emphasize such integrations as critical for the advancement of knowledge and patient welfare.
Closure
The conclusion of this article encapsulates the comprehensive examination of penile lymphedema, emphasizing its clinical significance and the need for increased awareness. Understanding this condition is crucial for healthcare professionals, as it directly impacts patient management and outcomes. In exploring the etiology, symptoms, and treatment options detailed throughout the article, we draw attention to the multifaceted nature of penile lymphedema.
Summarization of Key Points
- Definition: Penile lymphedema refers to the localized swelling of the penis due to impaired lymphatic drainage. Understanding its anatomy helps in grasping the full impact of lymphatic obstruction.
- Etiology: Factors can be congenital or acquired, which stresses the importance of comprehensive patient histories.
- Symptoms and Diagnosis: Recognizing the symptoms early and the use of imaging studies can lead to timely interventions.
- Management: A mix of conservative and, in some instances, surgical management methods are essential for effective treatment.
- Psychosocial Aspects: The psychosocial impact on patients, including mental health considerations and social stigmas, must not be overlooked.
This summary encapsulates the vital points that healthcare professionals and researchers need to consider while dealing with penile lymphedema. There is ample room for improvement in patient education and clinical management regarding this condition.
Call for Further Inquiry
Further research into penile lymphedema is necessary to enhance clinical practice and patient outcomes. Current knowledge lacks depth in several areas, including:
- Longitudinal Studies: There is a demand for studies tracking the progression of penile lymphedema over time. Understanding its natural course can inform better management strategies.
- Epidemiological Data: More data is needed to identify populations at risk, which can aid in prevention and early intervention strategies.
- Innovative Treatment Alternatives: Future research should focus on novel therapeutic options that may be more effective than current practices. New treatment modalities can significantly improve patient quality of life.
By emphasizing these areas, we encourage cooperation between researchers and clinicians to bring forth improved solutions and enhanced understanding of penile lymphedema. [Learn more about lymphedema on [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymphedema) or discuss in forums like [Reddit](https://www.reddit.com/).]



