Understanding Pleurisy of the Lungs: A Comprehensive Exploration

Intro
Pleurisy is an inflammatory condition that affects the pleura, which are the membranes surrounding the lungs. This condition can cause significant discomfort and can indicate underlying health concerns. Understanding the mechanisms and implications of pleurisy is essential for students, researchers, educators, and professionals who are engaged in health and respiratory studies. In this article, we will explore various aspects of pleurisy, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Key Concepts
Definition of Primary Terms
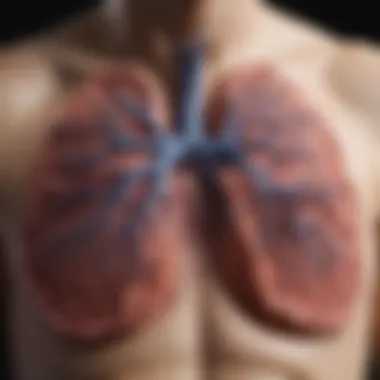
Pleurisy refers to inflammation of the pleura, the double-layered membrane that envelopes the lungs and lines the thoracic cavity. When the pleura becomes inflamed, it can cause sharp chest pain during breathing. This pain is often described as a result of the friction between the two layers of pleura.
Pleura are the tissues that separate the lungs from the chest wall while allowing for smooth movement during respiration.
Pleural effusion is another term related to pleurisy, which indicates the accumulation of excess fluid in the pleural space, often as a complication of the inflammatory process.
Related Concepts and Theories
The study of pleurisy is situated within a broader context of respiratory health. It is often correlated with:
- Pneumonia: Infection that can lead to pleurisy due to inflammation and fluid accumulation.
- Tuberculosis: A bacterial infection that may cause pleurisy and pleural effusion.
- Pulmonary embolism: A blockage in the pulmonary artery causing chest pain, which may mimic or accompany pleurisy.
Understanding these related concepts can provide insight into the complexities of pleurisy and its causative factors.
Future Directions
Gaps Identified in Current Research
Although significant strides have been made in understanding pleurisy, there remain areas that require further examination. Current literature shows:
- Limited longitudinal studies tracking the outcomes of pleurisy patients over time.
- An insufficient focus on the role of lifestyle factors, such as smoking and environmental exposures, in the incidence of pleurisy.
Suggestions for Further Studies
Future research could benefit from:
- Conducting multi-center studies to create a more comprehensive data set regarding pleurisy.
- Investigating the efficacy of novel treatment options, including pharmacological and holistic approaches to managing pleurisy symptoms.
Understanding pleurisy provides a crucial perspective on respiratory diseases and reinforces the importance of timely medical intervention to prevent complications.
Defining Pleurisy
Defining pleurisy is critical for understanding this health condition comprehensively. Pleurisy, an inflammation of the pleura, highlights important aspects of respiratory health. Knowing what pleurisy represents helps in recognizing its implications on overall wellness. The pleura are two thin membranes that line the chest cavity and cover the lungs. Their health is linked to respiratory function. Thus, understanding pleurisy is essential not just for medical professionals, but also for anyone interested in health matters.
Understanding the Pleura
The pleura consist of two layers: the visceral pleura, which covers the lungs, and the parietal pleura, which lines the chest wall. These layers create a cavity filled with pleural fluid, which acts as a lubricant. This fluid allows smooth movement of the lungs during breathing. The pleura also play a role in respiratory mechanics. Damage or inflammation can disrupt this balance, leading to pain and respiratory issues.
Understanding how the pleura function is vital for recognizing the symptoms and complications associated with pleurisy. If the pleura become inflamed, it can lead to friction between the layers, causing localized chest pain. This pain is often sharp and exacerbated by deep breaths or coughing. Thus, the health and integrity of the pleura are central to proper lung function.
What Is Pleurisy?
Pleurisy is an inflammatory condition of the pleura. It can be acute or chronic, and is often characterized by chest pain and difficulty breathing. The inflammation can arise from various causes, including infections, injury, or other systemic diseases. Because it affects the pleura, pleurisy can lead to complications such as pleural effusion, which is fluid accumulation in the pleural space.
Pleurisy can manifest quickly, leading to severe discomfort. Understanding its triggers and symptoms calls for attention to both individual health and broader health education.
The diagnosis and treatment of pleurisy are crucial for effective management. Recognizing the signs early can lead to prompt intervention. Understanding pleurisy enables awareness of risks and improves communication with healthcare providers. This aids in the prevention of chronic complications and improves quality of life.
In reviewing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pleurisy, one can better grasp its impact within the broader context of respiratory health.
Types of Pleurisy
Understanding the types of pleurisy is essential. Pleurisy may manifest in various forms, each characterized by unique features and implications. Recognizing these types informs effective treatment strategies and highlights their relevance in the context of overall lung health. The two primary types to be considered are acute pleurisy and chronic pleurisy.
Acute Pleurisy
Acute pleurisy, often arising suddenly, is a temporary condition typically caused by an infection or inflammation. Patients may experience sharp chest pain, often exacerbated by breathing movements, coughing, or sneezing. The pain usually prompts individuals to take shallow breaths to avoid discomfort, which may lead to complications like atelectasis, where parts of the lung collapse.
Key features of acute pleurisy include:
- Rapid onset: Symptoms can appear quickly, often within hours.
- Common causes: Bacterial or viral infections are frequent culprits. Pneumonia can also lead to acute inflammation of the pleura.
- Diagnosis: Patients may undergo imaging tests such as X-rays or CT scans to assess the extent of the inflammation and rule out other conditions.
In terms of treatment, acute pleurisy may involve pain relief medications and addressing the underlying cause. Antibiotics may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is identified. Understanding acute pleurisy is vital for early intervention and effective management, preventing potential complications that could arise from delayed treatment.
Chronic Pleurisy
Chronic pleurisy represents a more prolonged condition, defined by persistent inflammation of the pleura that lasts for weeks or even months. This type can stem from various underlying health issues, including autoimmune disorders, malignancy, or prolonged exposure to irritants. Differentiating chronic pleurisy from its acute counterpart is crucial in clinical settings, as the management strategies may significantly differ.
Characteristic aspects include:
- Long-term symptoms: Individuals may experience ongoing chest pain that varies in intensity and can be accompanied by other systemic symptoms.
- Underlying health issues: Chronic pleurisy can be a manifestation of other serious conditions, necessitating thorough medical evaluation to pinpoint the root cause.
- Potential for complications: This type may lead to pleural thickening, which can restrict lung function and increase the risk of further respiratory complications.
Treatment for chronic pleurisy often involves managing the underlying condition, alongside pain relief. Healthcare professionals may also explore procedural interventions such as thoracentesis if fluid buildup is present. It is critical to approach chronic pleurisy with a comprehensive treatment plan to optimize lung health and overall well-being.
Understanding the distinction between acute and chronic pleurisy enables healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans effectively, enhancing patient outcomes.
In summary, recognizing the different types of pleurisy allows individuals and healthcare professionals to better navigate the complexities of this condition. Immediate attention to symptoms of acute pleurisy and the sustained management of chronic pleurisy can lead to improved health outcomes and a better quality of life.
Causes of Pleurisy
Understanding the causes of pleurisy is crucial for both diagnosis and treatment. The causes are divided into two main categories: infectious and non-infectious. Each has distinct characteristics and implications. Being aware of these factors aids in recognizing pleurisy early, which can improve outcomes significantly. By understanding the roots of the condition, patients and healthcare providers can tailor management strategies effectively.


Infectious Causes
Infectious causes of pleurisy can arise from various microorganisms. Each type has unique features that affect the pleura, leading to inflammation and pain.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are among the most common causes of pleurisy. They usually occur when bacteria enter the pleural space, often as a complication of pneumonia or another respiratory infection. The key characteristic of this cause is that it typically involves severe symptoms. This makes it a crucial focus in this article. Understanding bacterial infections helps in prompt diagnosis and treatment. One unique feature of bacterial pleurisy is that it may lead to complications such as pleural effusion.
Advantages of identifying bacterial causes include the possibility of targeted treatment with antibiotics. However, the disadvantage is that if left untreated, it can result in serious health issues.
Viral Infections
Viral infections can also trigger pleurisy, often less severe than bacterial causes. Common viruses include the influenza virus and the herpes virus. A prominent characteristic of viral pleurisy is the occurrence alongside other viral symptoms, like fever and malaise. This makes it a relevant topic in this article.
The unique feature of viral infections is that antibiotics are ineffective against them. This adds complexity to the treatment process, as management focuses on symptom relief rather than eliminating the virus. The advantage is that viral infections tend to resolve on their own, while the disadvantage is the uncertainty surrounding recovery times.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections are relatively rare causes of pleurisy but can lead to significant complications, especially in immunocompromised individuals. Common fungi involved include Histoplasma and Coccidioides. The key characteristic is the chronic nature of symptoms, which can mimic tuberculosis. This relevance underscores its inclusion in this article.
A unique feature of fungal-related pleurisy is its association with specific geographic locations and environmental exposures. The advantage of identifying these infections early is prompt treatment with antifungal medications. However, the disadvantage is that they may require long treatment periods and can lead to serious complications if not managed properly.
Non-Infectious Causes
Non-infectious causes of pleurisy encompass a range of conditions. These causes are vital to explore, as they differ significantly from infectious causes and have different implications for treatment.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can result in pleurisy due to inflammation targeting the pleura. A distinctive characteristic of this cause is its link to other systemic symptoms. This makes it an important aspect of this article. Recognizing pleurisy related to autoimmune conditions can guide broader investigations into a patient's health.
The unique feature of autoimmune-related pleurisy is that it often accompanies chronic illnesses. The advantage of diagnosis is that treatments can be adjusted to manage both the pleurisy and the underlying autoimmune condition. The disadvantage is that patients may require lifelong management of their autoimmune disorder.
Trauma or Injury
Trauma or injury to the chest can result in pleurisy. This may occur due to accidents, falls, or surgical procedures. The key characteristic here is that the onset of symptoms is often acute and directly linked to the incident. This aspect provides context for its relevance in this article.
Unique to this cause is the immediate need for assessment following injury. Timely intervention is essential. The advantage is that treatment may lead to rapid improvements if the trauma is managed correctly. However, the disadvantage can be the risk of complications if injuries are not properly evaluated.
Malignancy
Malignancy, or cancer, can also lead to pleurisy, often as a consequence of tumor growth in the lungs. A significant characteristic of malignancy-associated pleurisy is that it often indicates advanced disease. This relevance makes it critical to discuss.
The unique feature of this cause involves the complexity of managing cancer along with pleurisy. The advantage is that recognizing the link between malignancy and pleurisy can facilitate comprehensive treatment plans. A notable disadvantage is that it may signal a poor prognosis, leading to difficult decisions regarding care and options.
Understanding these causes elucidates the complexity of pleurisy. Each cause has distinct pathways leading to inflammation in the pleura, impacting how pleurisy is experienced and treated. Recognizing these various facets plays a pivotal role in effective management, ensuring patients receive appropriate care and support.
Symptoms of Pleurisy
Understanding the symptoms of pleurisy is vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms serve as a crucial signal indicating the presence of underlying pleura inflammation. Recognizing these symptoms can lead patients to seek medical attention sooner, ultimately enhancing outcomes. The signs can vary, but they often include chest pain, difficulty breathing, and other related discomforts. Knowing how to identify and interpret these symptoms can empower patients and health providers in managing pleurisy effectively.
Chest Pain
Chest pain is often the most noticeable symptom of pleurisy. This pain can vary significantly in intensity and quality, sometimes making it difficult for individuals to articulate their experience.
Location of Pain
The location of pain is an important aspect to discuss. It typically manifests on one side of the chest, correlating with the affected pleura. This pain can feel sharp and may worsen during specific movements, such as deep breathing, coughing, or sneezing. The unilateral nature of the pain makes it a key indicator of pleurisy. Its distinct characteristic aids in differentiating pleurisy from other conditions like heart issues or gastrointestinal problems. For patients, understanding this location assists in ensuring they seek the right help.
Intensity and Duration
Intensity and duration of chest pain are also significant. The pain may be mild, causing discomfort, or severe, prompting urgent medical evaluation. It can be fleeting or persist over days. Recognizing this variability is crucial for patients. A severe and prolonged episode may indicate more significant complications requiring immediate attention. This understanding can lead to timely interventions.
Difficulty Breathing
Difficulty breathing, or dyspnea, often accompanies pleurisy. Patients may experience shortness of breath, particularly during physical activity or even at rest. This symptom can lead to increased anxiety for the patient, causing them to avoid exertion, which can affect their overall health. Difficulty breathing is not only uncomfortable; it can also exacerbate other underlying respiratory conditions. Therefore, understanding this symptom's seriousness assists in prioritizing medical evaluation.
Other Symptoms
Pleurisy often includes other symptoms that add complexity to its clinical presentation.
Fever and Chills
Fever and chills can indicate an underlying infection contributing to pleurisy, making this symptom noteworthy. These symptoms may accompany the chest pain and shortness of breath. The presence of fever is particularly vital as it helps to narrow down the potential causes behind pleurisy. While chills might be less frequently discussed, they can signify an acute inflammatory response. Identifying these symptoms allows clinicians to assess the severity and direct treatment strategies more effectively.
Cough
Coughing is another common symptom. It can vary in severity and may be dry or productive, depending on underlying causes, such as infections. A persistent cough can further irritate the pleura, heightening discomfort. Evaluating the cough's characteristics is essential for diagnosis, especially when determining if pleurisy arises from a primary respiratory infection.
Fatigue
Fatigue often accompanies pleurisy but is sometimes overlooked. Patients may feel unusually tired due to the body's response to inflammation and pain. While it is generally an expected symptom of many conditions, its presence in pleurisy emphasizes the overall burden on a patient's health. Acknowledging fatigue can help caregivers provide appropriate support and adjust interventions accordingly.
Diagnosis of Pleurisy
Diagnosing pleurisy is a critical phase in managing this respiratory condition. Proper diagnosis allows for an understanding of the underlying causes, guiding effective treatment strategies that can alleviate patient discomfort. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes, thus the precise diagnosis of pleurisy is important in reducing potential complications.
Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination serve as the first steps in diagnosing pleurisy. The physician gathers information regarding symptoms, past illnesses, and any recent injuries. Patients often describe sharp chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing, and a feeling of tightness in the chest. This pain is indicative and can help narrow down the possibilities.
In the physical examination, the doctor will listen to the lung sounds with a stethoscope. A characteristic pleural rub, which is a grating sound, may be heard if pleurisy is present. This sound occurs due to the inflamed pleura rubbing against each other. Physical exam findings combined with patient history enable the clinician to create an initial diagnostic impression, which can be further explored through additional testing.


Imaging Tests
Diagnostic imaging tests are essential for visualizing the condition of the lungs and pleura. Three commonly used imaging methods are X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds.
X-rays
X-rays are often the first imaging test performed. They provide an initial view of the lungs and can reveal abnormalities such as fluid buildup or inflammation in the pleura. X-rays are a quick and cost-effective choice, making them accessible for most patients. A unique feature of X-rays is their ability to show silhouette signs, which can indicate different lung issues. However, X-rays might not provide detailed information about subtle pleural changes, leading to further tests if abnormalities are suspected.
CT Scans
CT scans are more sophisticated and provide a detailed, cross-sectional view of the lung structures. This imaging method is especially beneficial in assessing pleural effusions and pleural thickening. CT scans are regarded as a gold standard in diagnosing pleurisy due to their ability to visualize structures that X-rays might miss. The high-resolution images allow for a better evaluation of the severity of pleural involvement. However, CT scans expose patients to higher radiation levels, which is a necessary consideration.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is increasingly recognized for its utility in diagnosing pleurisy, particularly for detecting pleural effusions. This imaging test is non-invasive and does not involve radiation. It is advantageous in guiding procedures like thoracentesis, where fluid is drawn from the pleural space. One of the unique features of ultrasound is its ability to dynamically assess the movement of the lungs and pleura during breathing, providing valuable real-time information. However, it may not provide comprehensive details about the lung parenchyma, limiting its effectiveness in some cases.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests also play a role in diagnosing pleurisy, specifically in identifying potential infections or inflammatory markers.
Blood Tests
Blood tests can aid in determining whether there is an underlying infection or inflammation. Markers such as C-reactive protein can indicate the presence of inflammation. These tests serve as a screening tool to prompt further investigation if needed. Blood tests are usually simple and quick, making them essential in the diagnostic process. Nevertheless, they are not diagnostic for pleurisy alone but can provide important supportive information.
Pleural Fluid Analysis
If pleural effusion is present, analyzing pleural fluid becomes essential. This analysis helps identify the nature of the fluid, whether it is transudate or exudate, which can point towards specific underlying causes of the effusion. Pleural fluid analysis is highly informative, revealing infections, malignancy, or other pathological processes. While it is an invasive procedure, it is often necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Pleurisy
Understanding the treatment options for pleurisy is crucial, as effective management can significantly alleviate symptoms and reduce complications. Treatment strategies can vary based on the underlying cause of pleurisy and the overall health condition of the patient. Options typically include medication and procedural interventions. Each method has its own set of benefits and considerations that impact a patient's recovery and well-being.
Medication
Medications play a significant role in the management of pleurisy. They help in reducing discomfort and addressing the underlying cause when applicable. Here, we discuss three primary types of medication used to treat pleurisy.
Pain Relievers
Pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are commonly used for managing pleuritic pain. The key characteristic of pain relievers is their ability to mitigate discomfort associated with pleurisy. These medications are a beneficial choice, as they can provide immediate relief to patients experiencing sharp chest pain.
The unique feature of pain relievers is their accessibility; they are often available over the counter. However, their effectiveness may vary depending on the individual, and excessive use can lead to side effects such as liver damage or gastrointestinal issues.
Anti-inflammatories
Anti-inflammatory medications, like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), target inflammation in the pleura. The primary aspect of anti-inflammatories is their dual capacity to reduce swelling and alleviate pain. They offer an important therapeutic approach for patients suffering from inflammatory pleurisy.
One characteristic that makes anti-inflammatories popular is their ability to address both pain and inflammation simultaneously. However, some patients may experience gastrointestinal upset or allergic reactions. Therefore, careful monitoring by healthcare providers is essential, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions.
Antibiotics (if bacterial)
Antibiotics are critical when pleurisy is caused by a bacterial infection. The specific aspect of antibiotics is their effectiveness in eliminating pathogenic bacteria. They are particularly beneficial when the primary cause of pleurisy is pneumonia or another bacterial infection.
Antibiotics' distinguishing feature is their ability to target specific bacteria, effectively eradicating the infection and reducing pleuritic symptoms. However, indiscriminate use can lead to antibiotic resistance. Therefore, it's essential that antibiotic treatment is guided by a thorough medical evaluation and, if necessary, laboratory tests.
Procedural Interventions
When medication alone is not sufficient to control symptoms or when complications arise, procedural interventions may be necessary. Two common procedures utilized in this context are Thoracentesis and Pleurodesis.
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis involves the insertion of a needle into the pleural space to remove excess fluid or air. This procedure is often indicated for pleuritic effusion, where fluid accumulation may be causing distress. Its key characteristic lies in its minimally invasive nature, providing quick relief from discomfort associated with the pressure of pleural effusions.
The unique feature of thoracentesis is its ability to both diagnose the cause of pleural effusion and treat it. While the benefits include immediate symptom relief, there are risks such as infection or pneumothorax. Careful patient selection and technique are critical in minimizing complications.
Pleurodesis
Pleurodesis is a procedure that aims to obliterate the pleural space to prevent future fluid accumulation. This can be particularly useful in patients with recurrent pleural effusions. The primary aspect of pleurodesis is that it addresses the underlying issue of fluid buildup, thus providing a longer-term solution compared to thoracentesis.
A key characteristic that makes pleurodesis a valuable intervention is its effectiveness in preventing recurrence of effusions after one treatment. However, it carries risks of pain and inflammation, and patients may require hospitalization following the procedure for monitoring. This procedure is typically reserved for more severe cases requiring a robust intervention.
In summary, understanding the treatment options for pleurisy is essential for managing this condition effectively. Both medication and procedural interventions have their pros and cons that depend on the patient's health status and condition severity. Timely treatment can play a critical role in preventing complications and improving outcomes.
Potential Complications of Pleurisy
Pleurisy, while primarily characterized by inflammation of the pleura, can lead to several complications that warrant careful consideration. Understanding these potential complications is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. The implications can vary from mild inconveniences to serious health issues, impacting long-term respiratory health and overall well-being.
Pleuritic Effusion
Pleuritic effusion occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the pleural space. This can happen as a direct consequence of pleurisy, leading to additional respiratory complications. The fluid can inhibit proper lung expansion, resulting in difficulty breathing and reduced oxygen intake.
Causes of Pleuritic Effusion
- Infection: Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause inflammation and subsequent fluid build-up.
- Cancer: Malignancies can lead to pleural effusion, either through direct tumor invasion or by causing substrate changes that increase fluid production.
- Heart Failure: Conditions that affect the heart's ability to pump effectively may also result in fluid retention, manifesting as pleural effusion.
Diagnosing pleuritic effusion typically involves imaging tests like chest X-rays or CT scans. If detected, thoracentesis, a procedure to drain the fluid, may be necessary to relieve symptoms and identify the underlying cause of the effusion.
Pleural Thickening
Pleural thickening refers to the scarring or thickening of the pleura that can result from persistent inflammation or chronic conditions. This complication can lead to long-term impairment of lung function, restricting the lungs' ability to expand fully and thereby reducing airflow.


Factors Contributing to Pleural Thickening
- Previous Infections: Episodes of pneumonia or other lung infections can contribute to the thickening of the pleura over time.
- Prolonged Inflammation: Chronic pleurisy stemming from conditions such as autoimmune disorders can result in permanent changes to the pleural surface.
- Asbestos Exposure: Known to cause various pleural diseases, asbestos can lead to severe thickening and fibrosis, necessitating careful monitoring and management.
Addresses the diagnostic aspects of pleural thickening may also utilize imaging techniques, including ultrasound or CT scans, to evaluate the extent of the condition. Treatment may involve addressing the underlying causes and potentially utilizing more invasive procedures in severe cases.
Understanding these complications aids in developing appropriate management strategies. In turn, this helps in preventing further deterioration of lung function, highlighting the critical importance of monitoring patients presenting with pleurisy.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing pleurisy is crucial for maintaining lung health and overall well-being. The awareness of risk factors and proactive measures can reduce the incidence of this inflammatory condition. Through effective prevention strategies, individuals can minimize their chances of developing pleurisy, especially those with underlying health conditions.
Vaccination
Vaccination plays a vital role in preventing infectious diseases that can lead to pleurisy. Some of the infections associated with pleurisy include pneumonia and influenza. Vaccines such as the pneumococcal vaccine and the seasonal flu vaccine help in building immunity against specific pathogens. By reducing the risk of infections, vaccination indirectly lowers the likelihood of pleurisy development. Several key points about vaccination include:
- Vaccines are proven methods to prevent serious diseases.
- Regular vaccination can significantly decrease the incidence of lung infections.
- Consult a healthcare provider regarding the suitability and timing of vaccinations for individuals with respiratory issues.
"Preventive health measures, like vaccination, pave the way for reducing the burden of infectious diseases that can complicate respiratory health."
Monitoring Chronic Conditions
Monitoring chronic conditions is essential for those at risk of pleurisy, particularly individuals with autoimmune disorders, lung diseases, or cardiovascular issues. Regular check-ups and management strategies can prevent complications that could lead to pleurisy. It is important to consider the following factors:
- Regular Health Check-ups: Continuous assessment of underlying conditions helps in early detection of issues that can worsen lung health.
- Adhering to Treatment Plans: Following prescribed treatment for chronic diseases can help in reducing exacerbations that may trigger pleurisy.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Promoting a healthy diet and physical activity contributes significantly to overall health. This acts as a preventive measure against complications of chronic diseases.
By focusing on prevention strategies such as vaccination and continuous monitoring of chronic conditions, individuals can effectively reduce their risk of pleurisy, ensuring long-term respiratory wellness.
Living with Pleurisy
Living with pleurisy requires a comprehensive understanding of how this condition interacts with daily life. It is essential to recognize the limitations and the support systems available for those affected. By acknowledging these factors, individuals can make informed decisions about their health and well-being, thereby aiding in their management of the disease.
Understanding Limitations
Pleurisy can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Symptoms like chest pain and difficulty breathing can hinder everyday activities. For many people, tasks that once seemed trivial become challenging. For example, strenuous exercises or even mild physical activity may provoke pain and discomfort. It’s essential for individuals to identify their physical limits.
Awareness and communication about one’s limitations can facilitate better interactions with family and friends. Healthcare providers must also be informed to create suitable management plans. Patients should not hesitate to engage with physical therapists to enhance respiratory function through guided exercises. Timely observation of symptoms can help in making necessary adjustments to activities, thus avoiding exacerbation of pleurisy.
Support and Resources
Support and resources play a vital role in helping individuals navigate the complexities associated with pleurisy.
Patient Support Groups
Patient support groups serve as a critical aspect of living with pleurisy. These groups offer a platform for individuals to share their experiences and coping strategies. The key characteristic of these groups is their ability to foster community among people who understand the unique challenges posed by pleurisy. Members often benefit from emotional encouragement and practical advice tailored to their experiences.
A unique feature of patient support groups is that they facilitate open dialogues about treatment options, personal journeys, and medical advice. By connecting with others dealing with similar conditions, individuals can gain new insights into managing their symptoms. This interconnectedness provides comfort and understanding, making it a popular choice for those affected.
Educational Resources
Educational resources are crucial in empowering individuals with knowledge regarding pleurisy. They provide accurate and up-to-date information about the condition, enhancing an understanding of management and treatment options. The key characteristic of these resources is their accessibility, often readily available through online platforms such as Wikipedia and Britannica.
A unique feature of educational resources lies in their ability to break down complex medical information into understandable terms. This clarity can significantly enhance an individual’s ability to make informed health choices. However, it is important to differentiate between reputable resources and those lacking scientific backing. Individuals should always cross-reference information with healthcare professionals to ensure reliability.
"Knowledge is power," especially when managing a condition like pleurisy, so leveraging these resources can often lead to better treatment outcomes and overall wellness.
In summary, understanding the limitations associated with pleurisy and utilizing available support structures is fundamental for those living with this condition. Both patient support groups and educational resources provide essential pathways for managing health effectively.
Additional information can be found on platforms like reddit.com and facebook.com, which may host groups focused on health issues.
Ongoing Research in Pleurisy
Ongoing research in pleurisy plays a critical role in advancing our understanding of this condition. As medical knowledge evolves, researchers explore various facets of pleurisy, focusing not only on treatment but also on prevention and diagnosis. These studies seek to elucidate the complexities of inflammatory processes affecting the pleura, aiming to improve patient outcomes through innovative approaches.
Advancements in Treatment
The field of pleurisy treatment has witnessed significant advancements over recent years. Researchers are investigating novel medications that target specific pathways involved in inflammation. This includes biologic therapies that can potentially reduce the reliance on traditional pain relief methods and anti-inflammatories. Some studies are focusing on using corticosteroids to address severe cases of pleurisy where inflammation is pronounced.
In addition, procedural interventions are also evolving. Techniques such as thoracentesis, which removes excess fluid from the pleural space, are being refined to enhance efficacy and patient comfort. Enhanced imaging technologies allow for better-guided procedures, minimizing complications and improving overall outcomes.
"As the understanding of pleurisy deepens, the hope for more targeted and less invasive treatments grows."
Exploring Underlying Mechanisms
Investigating the underlying mechanisms of pleurisy is crucial for establishing effective treatment protocols. Researchers are delving into how different pathogens, immune responses, and genetic factors contribute to the onset of pleurisy. Studies are examining the role of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators that signal cellular responses in pleural inflammation. This research helps illuminate why certain individuals are more susceptible to pleurisy and how varying immune responses can influence disease progression.
Moreover, understanding the connection between pleurisy and other respiratory conditions has become a focal point. Investigating comorbidities, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, allows for a more holistic approach to diagnosing and treating pleurisy. Collaborative research efforts are also emphasizing the importance of interdisciplinary studies, merging insights from pulmonology, immunology, and epidemiology.
By comprehending these mechanisms, healthcare providers can devise tailored strategies for prevention and management, ultimately leading to reduced complications and better health outcomes for patients suffering from pleurisy.
Finale
The conclusion of this article encapsulates the essential takeaways from our exploration of pleurisy, emphasizing the importance of understanding this condition. Grasping the nuances of pleurisy can guide individuals, healthcare professionals, and researchers in comprehending its impact on respiratory health. The knowledge shared here promotes informed health decisions and encourages proactive medical care. Moreover, recognizing the potential complications and symptoms associated with pleurisy is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Summary of Key Points
Throughout this article, key points include:
- Definition and Relevance: Pleurisy is an inflammatory condition affecting the pleura, crucial in respiratory function. Understanding its nature aids in appreciating its significance in lung health.
- Variety of Causes: Pleurisy can stem from infectious and non-infectious causes, each presenting unique challenges for patients and clinicians.
- Multi-faceted Symptoms: Symptoms like chest pain and difficulty breathing are pivotal in diagnosing and managing pleurisy effectively. Recognizing these symptoms ensures that individuals seek timely medical advice.
- Diagnostic Approaches: A combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging tests such as X-rays and CT scans, along with laboratory tests, forms a comprehensive approach to diagnose this condition accurately.
- Treatment Options: Therapeutic strategies range from medications to procedural interventions, highlighting the need for a tailored approach based on individual circumstances.
- Future of Research: Ongoing research continues to evolve, enhancing our understanding and treatment of pleurisy.
Future Perspectives
Looking ahead, advancements in the understanding of pleurisy are critical. Research is focusing on:
- Innovative Treatments: Development in medications and procedures that enhance recovery rates and improve quality of life for patients.
- Underlying Mechanisms: Investigations into the biological processes that lead to pleurisy could unveil preventative strategies or new treatment pathways.
- Patient Education and Support: Increasing awareness among patients and healthcare providers can lead to improved outcomes through earlier detection and management.



